Nutrition is the cornerstone of health, influencing every aspect of our physical and mental well-being. It encompasses the intake of nutrients from foods and beverages that our bodies need to function optimally. Understanding nutrition is essential for making informed choices that support long-term health, prevent chronic diseases, and promote overall vitality. This article explores the fundamental principles of nutrition, its key components, and practical tips for achieving a balanced and nutritious diet.
What is Nutrition?
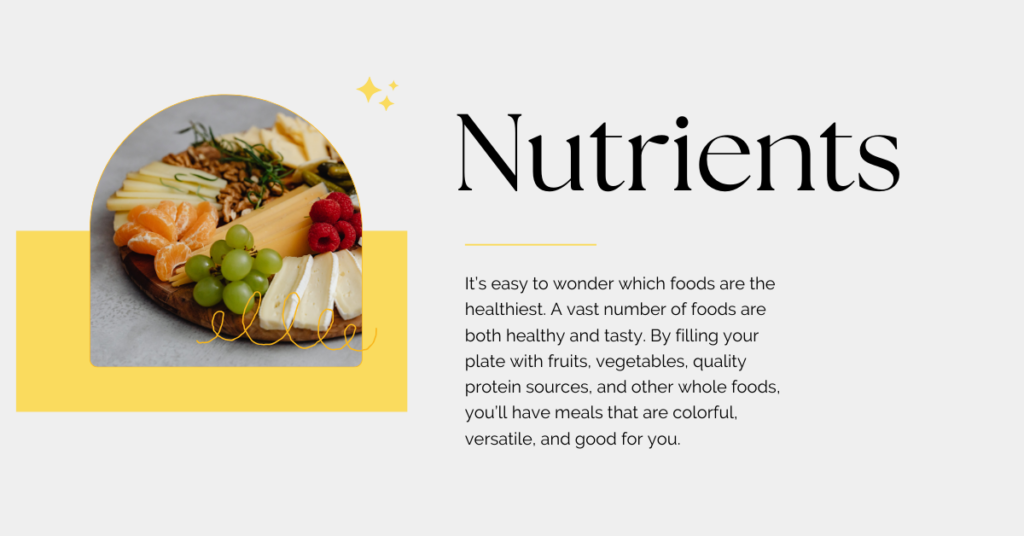
Nutrition refers to the process by which our bodies obtain and utilize the nutrients found in food. These nutrients are vital for growth, repair, and maintenance of bodily functions. A well-balanced diet provides the essential nutrients required for energy production, immune function, and the prevention of deficiencies and diseases.
Key Nutrients and Their Functions
- Macronutrients: These are nutrients required in larger amounts that provide energy and support bodily functions.
- Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source. They are found in foods such as grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which fuels bodily functions and physical activity.
- Proteins: Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues, making enzymes and hormones, and supporting immune function. Sources of protein include meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and nuts.
- Fats: Fats are crucial for energy storage, cell structure, and hormone production. They also aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). Healthy fat sources include avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish.
- Micronutrients: These are nutrients required in smaller amounts but are equally important for health.
- Vitamins: Vitamins play various roles in maintaining health, such as supporting immune function, vision, and skin health. For example:
- Vitamin C: Important for immune function and collagen synthesis.
- Vitamin D: Supports bone health and calcium absorption.
- Vitamin A: Essential for vision and immune function.
- Minerals: Minerals are involved in many physiological processes, including bone health, nerve function, and fluid balance. Key minerals include:
- Calcium: Vital for strong bones and teeth.
- Iron: Essential for oxygen transport in the blood.
- Potassium: Helps maintain fluid balance and normal cell function.
- Water: Although not a nutrient in the traditional sense, water is critical for life. It facilitates digestion, nutrient absorption, temperature regulation, and waste elimination. Staying hydrated is essential for maintaining overall health.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet ensures that you receive a variety of nutrients in the right proportions. This balance supports optimal health and helps prevent chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. Key principles of a balanced diet include:
- Variety: Consuming a wide range of foods ensures that you get a diverse array of nutrients. Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your diet.
- Moderation: Eating in moderation helps manage calorie intake and prevents overconsumption of any particular nutrient. Avoid excessive consumption of processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
- Proportion: Paying attention to portion sizes helps maintain a healthy weight and prevents overeating. Use portion control strategies and listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues.
Must Read : Understanding General Health: A Comprehensive Guide to Well-being
- Eat a Rainbow: Incorporate a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables into your diet. Different colors often indicate different nutrients and antioxidants.
- Choose Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains over refined grains to increase fiber intake and support digestive health.
- Incorporate Lean Proteins: Include sources of lean protein, such as chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes, to support muscle health and repair.
- Limit Added Sugars and Sodium: Reduce intake of foods and beverages high in added sugars and sodium to lower the risk of chronic diseases.
- Plan Meals: Planning and preparing meals in advance can help you make healthier choices and avoid reliance on convenience foods.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Aim for at least 8 cups (2 liters) of water daily, adjusting for activity level and climate.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how different foods make you feel and adjust your diet based on your energy levels, digestion, and overall well-being.
Conclusion
Nutrition is a fundamental aspect of health that influences every facet of our lives. By understanding the key nutrients, practicing a balanced diet, and adopting practical strategies for healthy eating, we can build a strong foundation for overall well-being. Prioritizing nutrition not only supports physical health but also enhances mental clarity, energy levels, and quality of life. Embracing a mindful approach to nutrition empowers us to make choices that nourish our bodies, support our goals, and contribute to a healthier, more vibrant life.

![Understanding Leukemia: A Comprehensive Overview [2024]](https://newstechblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/cancerHealth-1-1024x536.png)
![Coughing up Phlegm: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment [2024]](https://newstechblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Coughing-up-Phlegm-Causes-Symptoms-and-Treatment-1024x614.jpg)